Day 8: Building Your First Task Management API -
Ultra-Scalable Task Scheduler Implementation Series
The Problem We're Solving
Yesterday you built a database to store task definitions, but there's no way for external systems to interact with it. You need a bridge between the outside world and your task scheduler - a clean, professional API that can handle millions of requests. Every production system like Kubernetes, GitHub Actions, or AWS EventBridge uses REST APIs as their primary interface. Today, you're building that critical gateway.
The Critical Bridge Between Storage and Execution
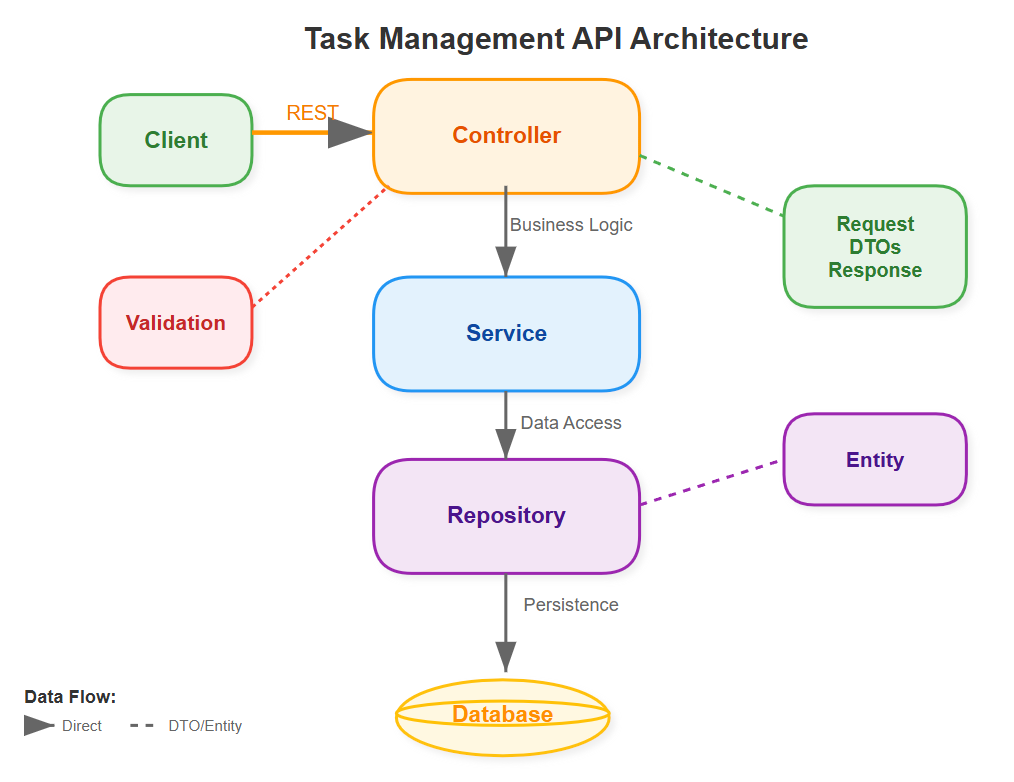
Yesterday, you built the foundation—a solid database layer for persisting task definitions. Today, we're constructing the bridge that connects the outside world to your task scheduler: a REST API. This isn't just about exposing endpoints; you're building the control interface that will eventually orchestrate millions of scheduled tasks.
Think of Kubernetes' API server—every pod, service, and deployment is managed through REST endpoints. Your Task Management API follows the same principle, becoming the single point of truth for task lifecycle operations.
Why REST APIs Matter in Distributed Task Scheduling
In production systems like Airflow or Kubernetes CronJobs, the API layer serves three critical functions:
1. Abstraction Boundary: Your API hides the complexity of database schemas and business rules behind clean, predictable interfaces.
2. Integration Point: External systems, monitoring tools, and future microservices will interact through these endpoints, not direct database access.
3. Validation Gateway: Every task definition gets validated at the API layer, preventing corrupt data from entering your system.